What is Mucus in Poo? Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and When to Worry
Finding mucus in your stool can be alarming. But before you panic, it’s essential to understand that a small amount of mucus in poo is perfectly normal. Mucus is a jelly-like substance produced throughout your digestive tract to keep it lubricated and functioning smoothly. However, a noticeable increase in the amount of mucus, or changes in its appearance, can signal an underlying health issue. This article will delve into the causes, symptoms, and when you should be concerned about mucus in your stool. We’ll explore different conditions that can lead to increased mucus production and provide guidance on when to seek medical attention.
The Role of Mucus in the Digestive System
Mucus plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. It acts as a protective barrier, shielding the delicate lining of the intestines from harsh stomach acids and digestive enzymes. This lubrication also helps stool pass through the digestive tract more easily. Without mucus, the intestines would be more susceptible to damage and inflammation. Therefore, a small amount of mucus in poo is a sign that your digestive system is functioning as it should. The key is to distinguish between a normal amount and an excessive amount that could indicate a problem.
Causes of Increased Mucus in Poo
Several factors can contribute to an increase in mucus in poo. While some causes are relatively benign, others may require medical intervention. Here are some common reasons why you might notice more mucus than usual:
Dietary Changes
Significant changes in your diet can temporarily increase mucus production. For example, consuming a large amount of high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can sometimes lead to more mucus in the stool. This is because fiber can irritate the intestinal lining as it passes through the digestive tract. Similarly, introducing new foods or eliminating certain foods from your diet can also disrupt the normal balance and lead to increased mucus production. In most cases, this is a temporary issue that resolves itself as your body adjusts to the dietary changes.
Dehydration
When you’re dehydrated, your body tries to conserve water, which can lead to drier stools. To compensate, your digestive system may produce more mucus to help the stool pass more easily. Ensuring you drink enough water throughout the day is crucial for maintaining healthy bowel movements and preventing excessive mucus production. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily, and more if you’re physically active or live in a hot climate.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that can cause a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits. Many people with IBS also experience increased mucus in their poo. The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but it’s believed to be related to problems with the way the brain and gut communicate. Stress, diet, and hormonal changes can all trigger IBS symptoms. Managing IBS often involves dietary modifications, stress reduction techniques, and medications to alleviate symptoms. [See also: Managing IBS Symptoms]
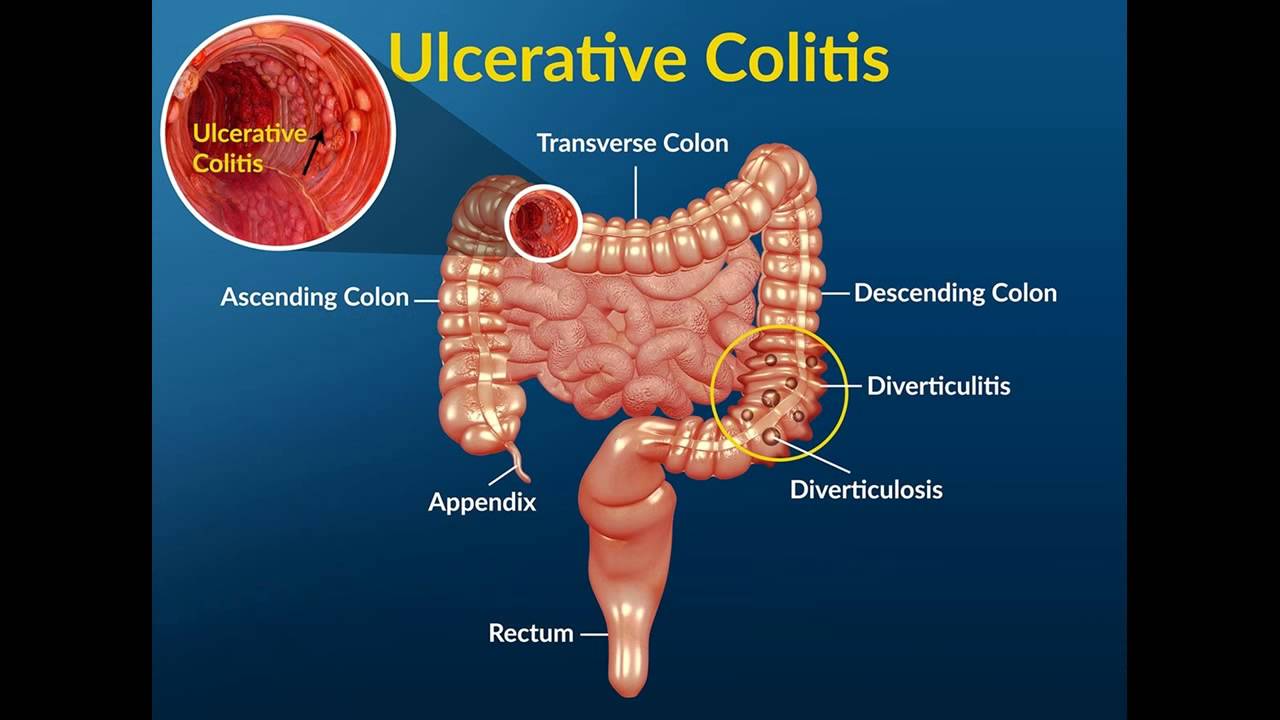
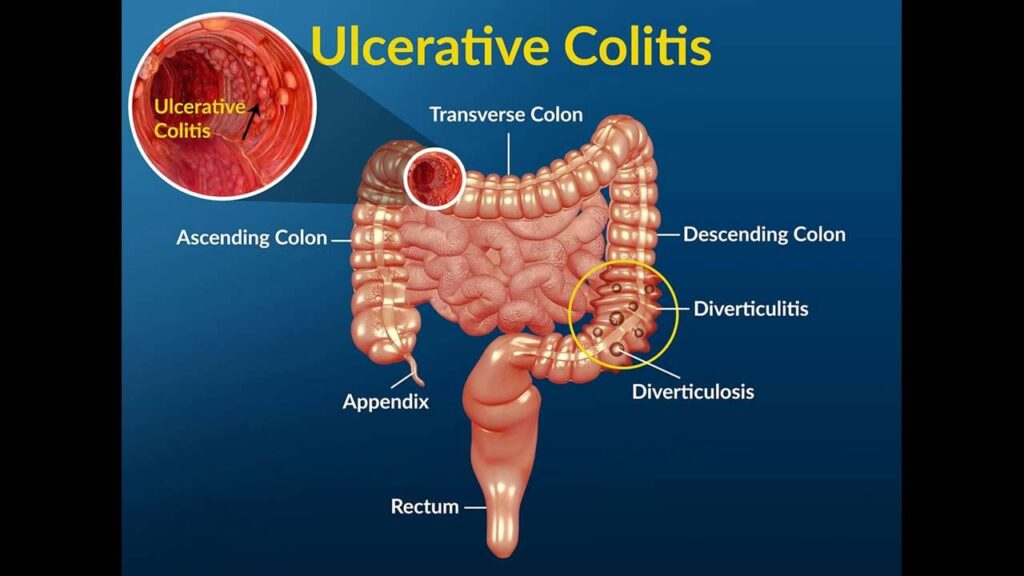
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a more serious condition than IBS. It encompasses chronic inflammatory disorders such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions cause inflammation and damage to the digestive tract, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and weight loss. Increased mucus in poo is a common symptom of IBD, often accompanied by blood. IBD requires ongoing medical management, including medications and sometimes surgery, to control inflammation and prevent complications.
Infections
Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can also cause an increase in mucus in poo. These infections can irritate the intestinal lining, leading to inflammation and increased mucus production. Common infections that can cause this include gastroenteritis (stomach flu), food poisoning, and parasitic infections like giardiasis. Symptoms of an infection may also include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. Treatment typically involves addressing the underlying infection with antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antiparasitic drugs.
Anal Fissures and Hemorrhoids
Anal fissures (small tears in the lining of the anus) and hemorrhoids (swollen veins in the rectum and anus) can also lead to increased mucus in poo. These conditions can cause irritation and inflammation, prompting the body to produce more mucus to protect the affected area. Symptoms may include pain during bowel movements, rectal bleeding, and itching. Treatment options range from topical creams and suppositories to more invasive procedures like surgery.
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that affects the lungs and digestive system. It causes the body to produce thick, sticky mucus that can clog the airways and digestive tracts. People with CF often have difficulty absorbing nutrients from food, leading to malnutrition and other health problems. Increased mucus in poo is a common symptom of CF, reflecting the overall disruption of mucus production in the body. Management of CF involves a multidisciplinary approach, including medications, therapies, and dietary modifications.
Colon Cancer
In rare cases, increased mucus in poo can be a sign of colon cancer. Colon cancer can cause inflammation and irritation in the colon, leading to increased mucus production. Other symptoms of colon cancer may include changes in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, and unexplained weight loss. It’s essential to see a doctor if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you have a family history of colon cancer. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes.
Symptoms Associated with Mucus in Poo
The symptoms you experience along with mucus in poo can provide valuable clues about the underlying cause. Here are some symptoms to watch out for:
- Abdominal Pain: This can indicate inflammation, infection, or IBS.
- Diarrhea: Frequent, loose stools can be a sign of infection, IBD, or dietary issues.
- Constipation: Difficulty passing stools may be related to dehydration or IBS.
- Rectal Bleeding: Blood in the stool can indicate IBD, anal fissures, hemorrhoids, or colon cancer.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a sign of IBD, colon cancer, or other serious conditions.
- Fever: Fever suggests an infection.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms often accompany infections or food poisoning.
When to See a Doctor About Mucus in Poo
While a small amount of mucus in poo is usually not a cause for concern, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- A significant increase in the amount of mucus.
- Mucus accompanied by blood.
- Persistent abdominal pain.
- Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea or constipation) that last for more than a few days.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fever.
- A family history of colon cancer or IBD.
Your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms and medical history. They may also order tests to help determine the cause of the mucus in your stool. These tests may include:
- Stool Sample: To check for infections, parasites, or blood.
- Colonoscopy: To examine the colon for inflammation, polyps, or other abnormalities.
- Sigmoidoscopy: Similar to a colonoscopy, but only examines the lower part of the colon.
- Blood Tests: To check for signs of inflammation or infection.
Treatment Options for Mucus in Poo
The treatment for mucus in poo depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options:
- Dietary Changes: Adjusting your diet to avoid trigger foods or increase fiber intake can help manage IBS and other digestive issues.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining healthy bowel movements.
- Medications: Depending on the cause, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or other medications to alleviate symptoms.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat conditions like colon cancer or severe IBD.
Preventing Excessive Mucus in Poo
While not all causes of increased mucus in poo are preventable, there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently to prevent infections.
- Manage Stress: Stress can trigger digestive issues, so find healthy ways to manage stress.
- Get Regular Checkups: Regular checkups can help detect and treat underlying health problems early.
Conclusion
Finding mucus in poo can be concerning, but it’s important to remember that a small amount is often normal. However, if you notice a significant increase in the amount of mucus, or if it’s accompanied by other symptoms like abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, or changes in bowel habits, it’s essential to see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve your overall health. Understanding the potential causes of mucus in your stool and knowing when to seek medical attention can empower you to take control of your digestive health. Remember, paying attention to your body and seeking professional advice when needed is crucial for maintaining a healthy and happy life. The presence of mucus in poo isn’t always alarming, but it warrants attention to ensure your well-being. Don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns about mucus in poo. Addressing the issue promptly can lead to effective management and peace of mind. Monitoring your bowel movements and noting any changes, including the amount of mucus in poo, is a good practice for overall health. Remember that mucus in poo can sometimes be a sign of an underlying condition, so it’s always better to be proactive. If you’re worried about mucus in poo, seeking medical advice is the best course of action. The presence of mucus in poo can vary from person to person, but significant changes should be investigated. Keep track of your symptoms related to mucus in poo to provide your doctor with a comprehensive overview. Ignoring mucus in poo when accompanied by other symptoms can delay necessary treatment. Understanding the possible causes of mucus in poo can help you make informed decisions about your health. Regular monitoring of your bowel movements and awareness of mucus in poo can aid in early detection of potential issues. When in doubt, always consult a healthcare professional regarding mucus in poo and related symptoms. The appearance of mucus in poo can sometimes indicate dietary imbalances or other manageable factors. Be vigilant about changes in your bowel movements, including the presence of mucus in poo, and seek medical advice when necessary. Addressing concerns about mucus in poo promptly can contribute to better digestive health and overall well-being.