The Ultimate Guide to Fox Farm Ocean Forest Feeding Schedule
Fox Farm Ocean Forest is a popular choice for growers seeking a nutrient-rich and well-draining soil mix. Understanding the correct Fox Farm Ocean Forest feeding schedule is crucial for maximizing plant health and yield. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to properly feed your plants when using this soil, ensuring they receive the right nutrients at the right time.
Understanding Fox Farm Ocean Forest Soil
Fox Farm Ocean Forest is a soilless mix, primarily composed of sphagnum peat moss, earthworm castings, fish emulsion, and crab meal. This combination provides a robust blend of nutrients right out of the bag. The initial nutrient load often eliminates the need for additional feeding for several weeks, particularly for young plants. However, as plants grow and deplete these initial nutrients, supplementing with a carefully planned Fox Farm Ocean Forest feeding schedule becomes essential.
Nutrient Content and pH Levels
The nutrient composition of Fox Farm Ocean Forest typically includes a balanced mix of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), along with micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and iron. The pH level is generally maintained between 6.3 and 6.8, which is ideal for most plants. Regular monitoring of pH levels is recommended to ensure optimal nutrient absorption. Using a reliable pH meter can help maintain the correct balance and prevent nutrient lockout.
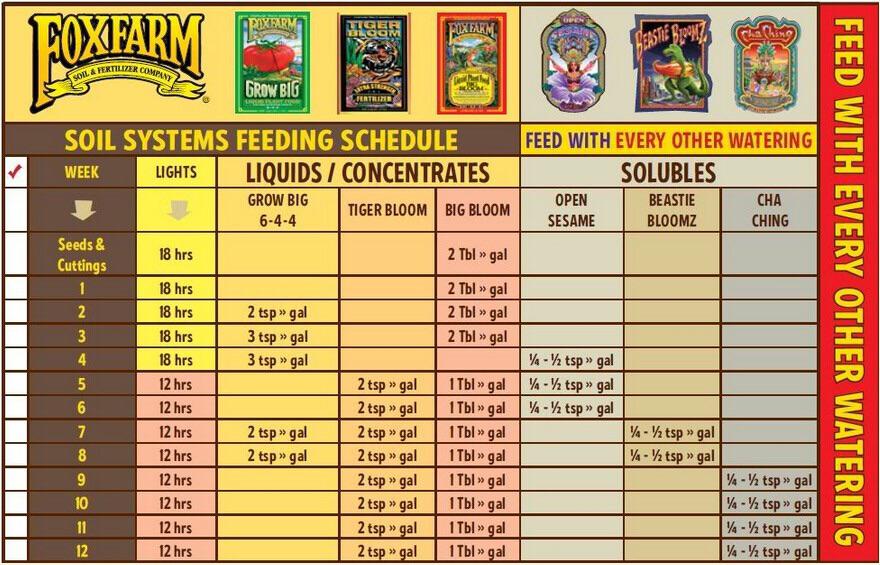
Creating a Fox Farm Ocean Forest Feeding Schedule
Developing an effective Fox Farm Ocean Forest feeding schedule requires careful consideration of several factors, including the plant species, growth stage, and environmental conditions. Here’s a general guideline to get you started:
Week 1-3: Initial Growth Stage
During the first few weeks after transplanting into Fox Farm Ocean Forest, most plants will not require additional nutrients. The soil is typically rich enough to sustain them during this initial growth phase. Monitor your plants closely for signs of nutrient deficiency, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth. If deficiencies are observed, a light feeding with a balanced nutrient solution may be necessary. However, avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to nutrient burn.
Week 4-6: Vegetative Stage
As plants enter the vegetative stage, their nutrient demands increase. Begin supplementing with a nutrient solution formulated for vegetative growth. Fox Farm offers a range of products specifically designed for this purpose, such as Grow Big. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, starting with a lower concentration and gradually increasing it as needed. A typical Fox Farm Ocean Forest feeding schedule during this stage might involve feeding every other watering, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between applications.
Week 7-9: Transition to Flowering Stage
The transition from the vegetative to the flowering stage requires a shift in nutrient ratios. Gradually reduce the nitrogen levels and increase the phosphorus and potassium levels to support flower development. Fox Farm Tiger Bloom is a popular choice for this stage. Continue to monitor your plants closely and adjust the feeding schedule based on their specific needs. Consider using a bloom booster to enhance flower production. [See also: Understanding Plant Nutrient Requirements]
Week 10+: Flowering Stage
During the flowering stage, plants require a higher concentration of phosphorus and potassium to support bud development and ripening. Continue using Tiger Bloom, and consider adding additional supplements such as Big Bloom to enhance flavor and aroma. A well-executed Fox Farm Ocean Forest feeding schedule during this stage will result in larger, more potent flowers. Flush the soil with plain water a week or two before harvest to remove any remaining nutrients and improve the overall quality of the final product.
Tips for Optimizing Your Feeding Schedule
- Monitor pH Levels: Regularly check the pH of your soil and nutrient solution to ensure optimal nutrient absorption. Aim for a pH between 6.3 and 6.8.
- Avoid Over-Fertilizing: Over-fertilizing can lead to nutrient burn and other problems. Start with a lower concentration of nutrients and gradually increase it as needed.
- Flush the Soil: Periodically flush the soil with plain water to remove any accumulated salts and prevent nutrient lockout.
- Observe Your Plants: Pay close attention to your plants and adjust the feeding schedule based on their specific needs. Look for signs of nutrient deficiency or toxicity, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or burned leaf tips.
- Use Quality Water: The quality of your water can affect nutrient absorption and plant health. Use filtered or distilled water whenever possible to avoid any unwanted contaminants.
Fox Farm Feeding Chart Example
While the exact Fox Farm Ocean Forest feeding schedule will vary depending on your specific plants, here’s a general example:
- Week 1-3: No additional nutrients needed.
- Week 4-6 (Vegetative): Grow Big (1/2 strength) every other watering.
- Week 7-9 (Transition): Grow Big (1/4 strength) and Tiger Bloom (1/2 strength) every other watering.
- Week 10+ (Flowering): Tiger Bloom (full strength) and Big Bloom (full strength) every other watering.
- Pre-Harvest: Flush with plain water for 1-2 weeks.
Always adjust these recommendations based on your plant’s specific needs and environmental conditions. [See also: Common Plant Diseases and Prevention]
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Nutrient Burn
Nutrient burn is a common issue caused by over-fertilizing. Symptoms include yellowing or browning leaf tips, stunted growth, and overall plant stress. To address nutrient burn, flush the soil with plain water to remove excess nutrients. Reduce the concentration of your nutrient solution and monitor your plants closely.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Nutrient deficiencies can occur if plants are not receiving enough of a particular nutrient. Symptoms vary depending on the specific nutrient deficiency, but may include yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and abnormal leaf patterns. To address nutrient deficiencies, identify the deficient nutrient and supplement with a balanced nutrient solution. Consider performing a soil test to determine the exact nutrient levels in your soil.
pH Imbalance
pH imbalance can affect nutrient absorption and lead to various plant health issues. Regularly monitor the pH of your soil and nutrient solution and adjust as needed. Use pH up or pH down solutions to maintain the optimal pH range of 6.3 to 6.8.
Alternative Feeding Methods
While liquid nutrients are a common choice for supplementing Fox Farm Ocean Forest, other feeding methods can also be effective. These include:
- Top Dressing: Applying dry amendments to the soil surface, such as bone meal or blood meal, can provide a slow-release source of nutrients.
- Compost Tea: Brewing compost tea can provide a beneficial blend of nutrients and microorganisms.
- Foliar Feeding: Applying nutrients directly to the leaves can provide a quick boost of essential elements.
Conclusion
Mastering the Fox Farm Ocean Forest feeding schedule is essential for achieving optimal plant health and yield. By understanding the nutrient content of the soil, monitoring your plants closely, and adjusting the feeding schedule as needed, you can ensure that your plants receive the right nutrients at the right time. Remember to avoid over-fertilizing, maintain proper pH levels, and flush the soil periodically to prevent nutrient lockout. With careful planning and attention to detail, you can maximize the potential of Fox Farm Ocean Forest and achieve impressive results. This detailed guide should provide a solid foundation for your Fox Farm Ocean Forest feeding schedule.
