Understanding States with Delegates: A Comprehensive Guide
In the United States’ political landscape, the allocation of delegates to each state plays a pivotal role in presidential elections. Understanding how states with delegates are structured and how these delegates influence the nomination process is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp the intricacies of American democracy. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the delegate system, exploring its mechanics, historical context, and contemporary relevance.
The Electoral College and Delegate Allocation
The Electoral College is a constitutionally mandated body that elects the President and Vice President of the United States. Instead of directly voting for a candidate, citizens vote for a slate of electors who then cast the actual votes. Each state is allocated a number of electors equal to its total number of representatives in Congress (House of Representatives + Senate). This system ensures that states with delegates have a say in the presidential election, albeit indirectly.
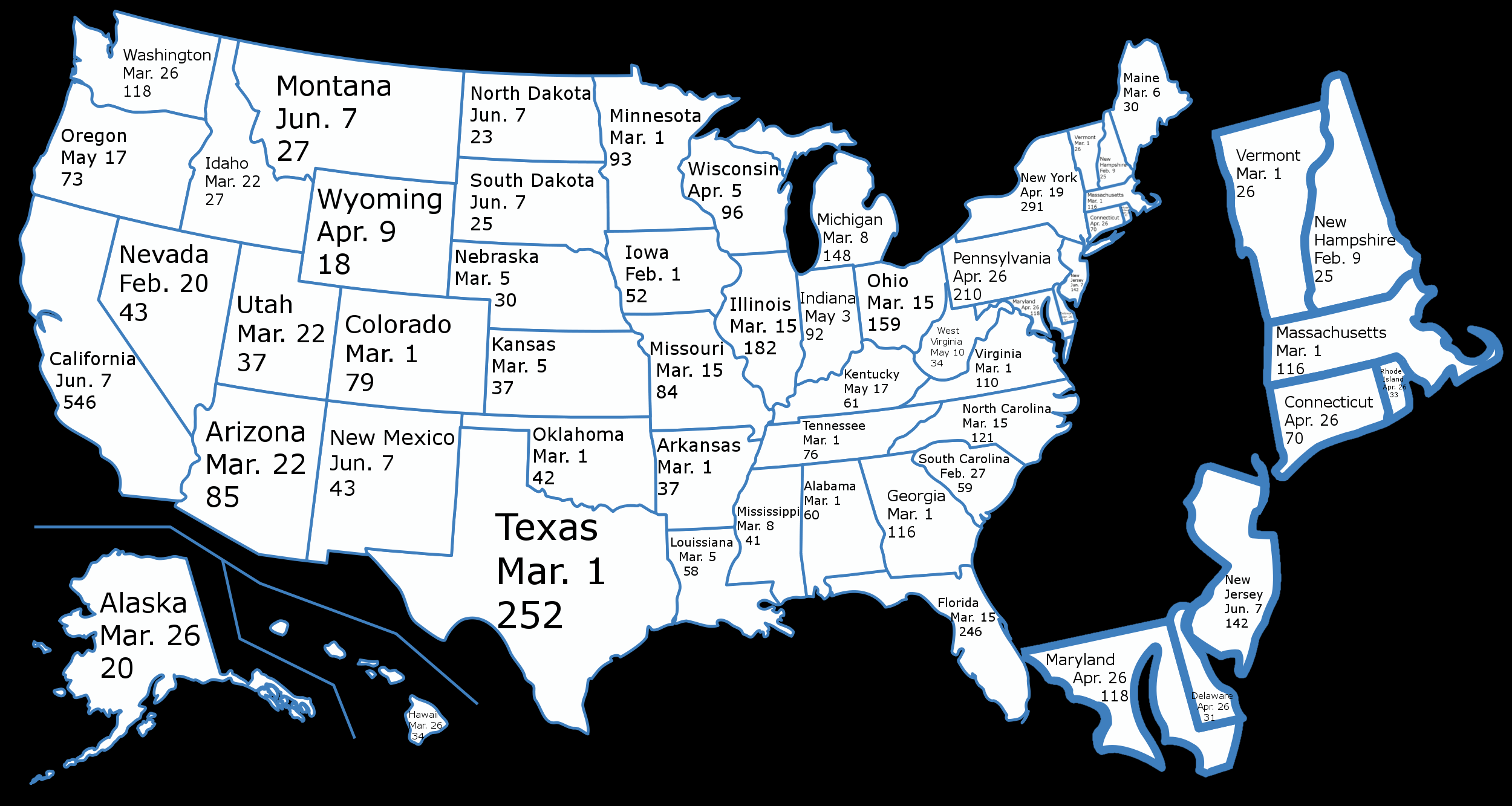
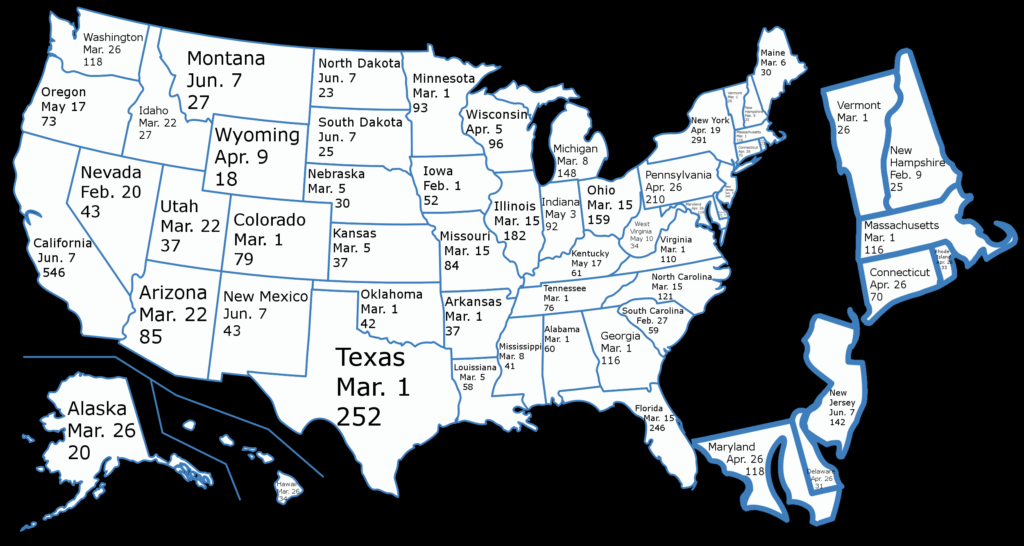
The allocation of delegates to each state is based on population. States with larger populations receive more electoral votes, reflecting their greater representation in Congress. This means that states with delegates like California, Texas, Florida, and New York wield considerable influence in presidential elections due to their high number of electoral votes.
Primary Elections and Delegate Selection
Before the general election, each political party conducts primary elections or caucuses to select their presidential nominee. During these primaries, voters in each state cast ballots for their preferred candidate. The results of these primary elections determine how the state’s delegates will be allocated to the various candidates. The process of selecting these delegates varies significantly from state to state, adding another layer of complexity to understanding states with delegates.
Types of Delegates
There are generally two types of delegates: pledged and unpledged. Pledged delegates are bound to vote for a specific candidate based on the results of the primary election or caucus. Unpledged delegates, also known as superdelegates (primarily in the Democratic Party), are not bound to any particular candidate and can vote for whomever they choose at the national convention. The number of superdelegates has decreased in recent years due to reforms aimed at increasing the influence of grassroots voters. Understanding the distinction between pledged and unpledged delegates is critical when analyzing states with delegates and their impact on the nomination process.
Delegate Allocation Methods
States with delegates employ different methods for allocating delegates to candidates. Some states use a winner-take-all system, where the candidate who wins the most votes in the primary receives all of the state’s delegates. Other states use a proportional system, where delegates are allocated proportionally based on the percentage of votes each candidate receives. There are also variations and hybrid systems that combine elements of both. For instance, a state might have a threshold requirement, where a candidate must receive a certain percentage of the vote to be eligible for any delegates. The specific method used by each state can significantly impact the outcome of the primary election and the overall delegate count for each candidate. Therefore, it is essential to understand the delegate allocation methods used in states with delegates.
The Role of Delegates at National Conventions
The culmination of the primary election season is the national convention, where delegates from each state gather to formally nominate their party’s presidential and vice-presidential candidates. At the convention, delegates cast their votes based on the results of the primary elections and caucuses. If a candidate secures a majority of the delegates, they are declared the party’s nominee. However, in some cases, no candidate may have a majority of delegates going into the convention, leading to a contested or brokered convention. In such scenarios, delegates may engage in negotiations and horse-trading to reach a consensus on a nominee. The actions of delegates at national conventions can have a profound impact on the outcome of the election. Therefore, understanding the role of delegates in states with delegates is crucial.
Historical Context and Evolution
The delegate system has evolved significantly over time. In the early days of the United States, presidential nominations were often decided by party elites in smoke-filled rooms. As democracy expanded, primary elections and caucuses became more common, giving ordinary voters a greater say in the nomination process. Reforms in the 1970s, spurred by concerns about the lack of transparency and representativeness in the delegate selection process, led to the adoption of more open and democratic procedures. These reforms aimed to empower grassroots voters and reduce the influence of party bosses. The ongoing debate over the role of superdelegates in the Democratic Party reflects the continuing tension between the desire for a more democratic process and the desire to ensure that the party nominates a candidate who is electable. Examining the historical evolution of the delegate system in states with delegates provides valuable insights into the changing dynamics of American politics.
Contemporary Relevance and Challenges
The delegate system continues to be a subject of debate and reform. Critics argue that the system is too complex, opaque, and undemocratic, while supporters argue that it serves as a valuable check on the power of individual voters and ensures that the party nominates a candidate who is broadly acceptable to its members. Recent controversies over the role of superdelegates and the allocation of delegates in certain states have highlighted the need for further reforms to enhance transparency and ensure fairness. Furthermore, the increasing polarization of American politics has made it more difficult to reach consensus on reforms to the delegate system. Understanding the contemporary challenges facing the delegate system in states with delegates is essential for informed civic engagement.
The distribution of delegates among states with delegates significantly impacts the strategies employed by presidential candidates. Candidates often focus their resources and attention on states with a large number of delegates, such as California, Texas, and Florida. These states are often referred to as “battleground states” because they can significantly influence the outcome of the election. Candidates may also target smaller states with early primary elections, such as Iowa and New Hampshire, to gain momentum and build name recognition. The strategic considerations involved in campaigning in states with delegates highlight the importance of understanding the delegate system.
The delegate system is a complex and multifaceted aspect of American democracy. Understanding how states with delegates are structured, how delegates are selected, and how they influence the nomination process is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp the intricacies of presidential elections. By examining the historical context, contemporary relevance, and ongoing debates surrounding the delegate system, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities facing American democracy. As the political landscape continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed about the delegate system and its impact on the future of American politics.
In conclusion, the system of states with delegates is a cornerstone of the American presidential election process. Its complexities and nuances require careful consideration to fully understand its impact on the selection of presidential nominees and the overall political landscape. By understanding the allocation, selection, and role of delegates, citizens can be more informed participants in the democratic process. The influence of states with delegates cannot be overstated, and staying informed about its workings is vital for every engaged citizen.
The process in states with delegates is subject to constant scrutiny and reform, reflecting the ongoing quest to balance democratic ideals with practical political considerations. Whether through primary elections, caucuses, or national conventions, the delegates play a critical role in shaping the future leadership of the nation. As such, the study and understanding of states with delegates remain essential for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of American political life.
The future of states with delegates will likely involve continued debates about fairness, representation, and the balance of power between grassroots movements and established political structures. As the electorate evolves and new challenges arise, the system will need to adapt to ensure it continues to serve its purpose: selecting the most qualified and representative candidates for the highest office in the land. Therefore, ongoing engagement with the dynamics of states with delegates is crucial for maintaining a healthy and vibrant democracy.
Understanding the process involving states with delegates is fundamental to understanding the American presidential election. The allocation, selection, and influence of delegates shape the nomination process and play a crucial role in determining who will lead the nation. By staying informed and engaged, citizens can contribute to a more transparent and representative democratic process. The system of states with delegates is a dynamic and evolving aspect of American politics, and its ongoing study is essential for informed civic participation.
[See also: Understanding the Electoral College]
[See also: Primary Elections Explained]
[See also: The Role of Superdelegates]