What Do Search Engines Do? Unveiling the Core Functions
In today’s digital age, search engines are indispensable tools for navigating the vast expanse of the internet. But what do search engines do exactly? Beyond simply providing a list of links in response to a query, search engines perform a complex set of functions to organize and deliver relevant information. Understanding these functions is crucial for anyone seeking to effectively utilize the internet, whether for research, commerce, or simple curiosity. This article delves into the core operations of search engines, explaining how they crawl, index, rank, and ultimately, answer our questions.
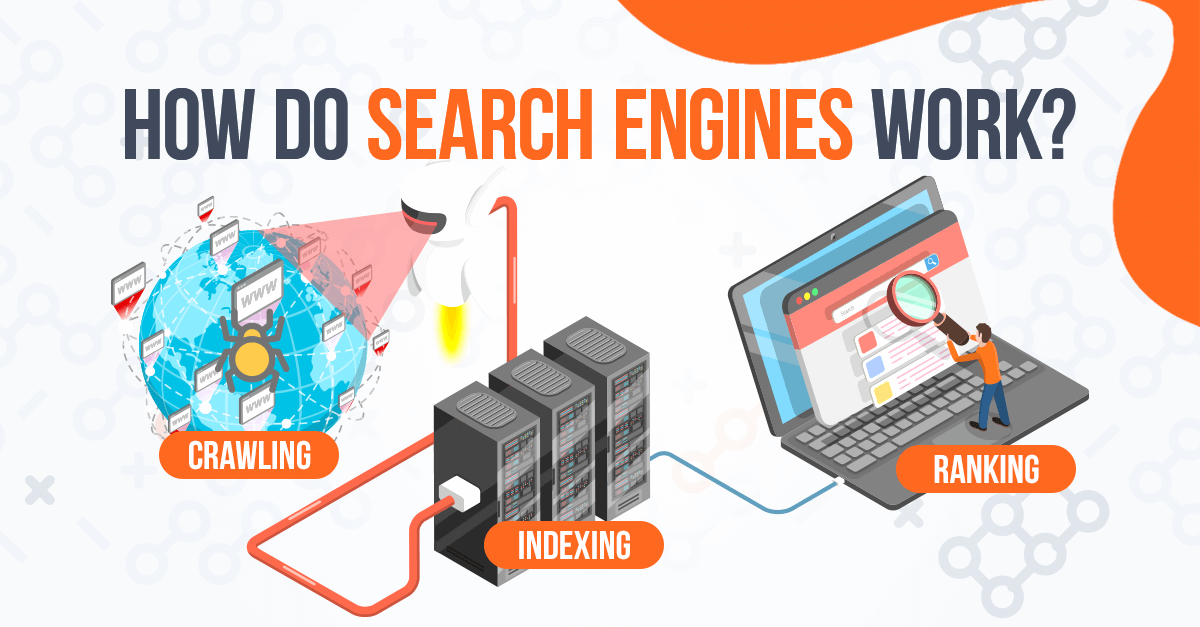
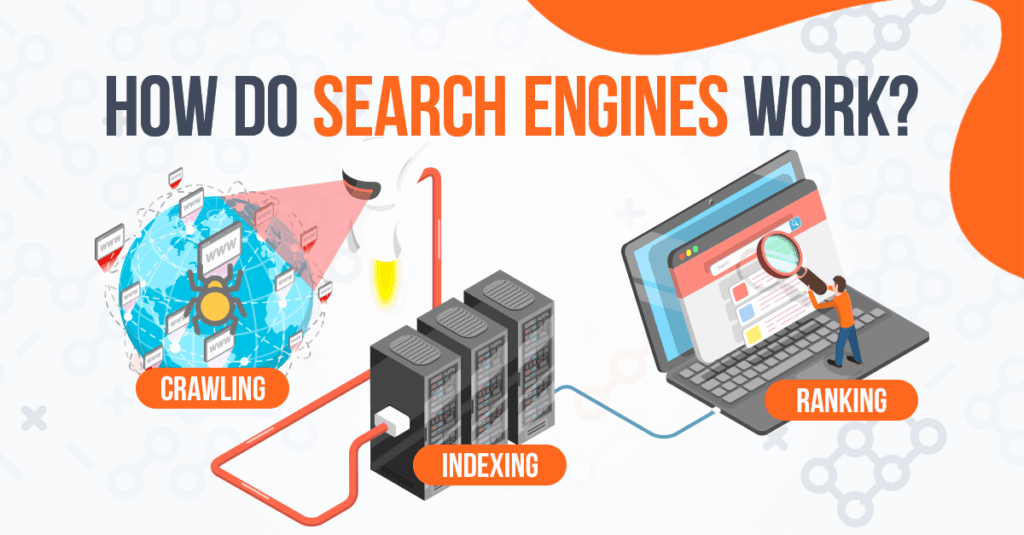
Crawling: Exploring the Web
The first crucial step in the search engine process is crawling. Think of it as the exploratory phase where search engines use automated programs, often called “crawlers,” “spiders,” or “bots,” to discover new and updated content on the web. These crawlers follow links from one webpage to another, systematically traversing the internet’s intricate network. When a crawler lands on a page, it analyzes the content, including text, images, videos, and metadata. This information is then used to understand what the page is about.
The crawling process is continuous. Search engines constantly revisit previously crawled pages to check for updates and new links. This ensures that the search engine’s index remains current and reflects the ever-changing landscape of the web. The frequency with which a page is crawled depends on various factors, including its importance, update frequency, and the number of links pointing to it. Websites can also use a file called `robots.txt` to instruct crawlers which parts of their site should or should not be crawled, helping to manage crawl budget and prevent overloading the server.
Indexing: Organizing the Information
Once a page has been crawled, the information extracted from it needs to be organized. This is where indexing comes in. Indexing is the process of analyzing the crawled content and adding it to a massive database, often referred to as the search engine’s index. This index is like a library catalog, allowing the search engine to quickly locate relevant pages when a user submits a query.
During indexing, search engines analyze the text on a page, identify keywords, and extract other relevant information, such as the page’s title, meta description, and headings. They also consider factors like the page’s structure, the use of headings, and the presence of images and videos. The search engine then creates an entry for the page in its index, associating it with the identified keywords and other relevant information. This process allows the search engine to efficiently retrieve relevant pages based on user queries. The index is constantly updated as new pages are crawled and existing pages are updated.
Ranking: Determining Relevance and Quality
When a user submits a query, the search engine uses its index to identify pages that are relevant to the query. However, the search engine typically finds thousands or even millions of pages that contain the keywords in the query. The challenge is to present the most relevant and high-quality pages to the user in the order that is most likely to satisfy their information need. This is where ranking comes in.
Ranking is the process of ordering the search results based on various factors, including relevance, authority, and user experience. Search engines use complex algorithms to evaluate each page and assign it a ranking score. These algorithms take into account hundreds of different factors, including:
- Relevance: How closely the page’s content matches the user’s query.
- Authority: The credibility and trustworthiness of the page, often measured by the number and quality of links pointing to it.
- User Experience: Factors such as page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and the presence of intrusive ads.
- Content Quality: The depth, accuracy, and originality of the content on the page.
- Freshness: How recently the page has been updated.
The ranking algorithms are constantly evolving as search engines strive to improve the quality of their search results. They are also designed to prevent manipulation by website owners who try to artificially inflate their rankings. [See also: Understanding Search Engine Algorithms] The pages with the highest ranking scores are displayed at the top of the search results page, while those with lower scores are displayed lower down or not at all.
Answering Queries: Delivering Information to Users
The ultimate goal of a search engine is to answer users’ queries by providing them with the information they are seeking. This involves not only retrieving relevant pages but also presenting them in a way that is easy to understand and access. Search engines use various techniques to enhance the user experience, including:
- Snippets: Short summaries of the page’s content that appear in the search results.
- Featured Snippets: Direct answers to specific questions, displayed prominently at the top of the search results.
- Knowledge Panels: Information boxes that provide quick facts about people, places, and things.
- Image and Video Results: Visual content that is relevant to the user’s query.
- Local Search Results: Results that are relevant to the user’s location.
By providing these features, search engines aim to deliver the most relevant and useful information to users as quickly and efficiently as possible. They are constantly experimenting with new ways to improve the user experience and make it easier for people to find what they are looking for. What do search engines do? They strive to be the most helpful and reliable source of information on the internet.
The Importance of Understanding Search Engine Functions
Understanding what do search engines do is vital for several reasons. For individuals, it allows for more effective searching, leading to quicker and more accurate results. By knowing how search engines work, users can formulate their queries in a way that is more likely to yield relevant information. They can also critically evaluate the search results and identify the most credible sources. [See also: Advanced Search Techniques]
For businesses and website owners, understanding search engine functions is essential for search engine optimization (SEO). By optimizing their websites for search engines, they can improve their visibility in search results and attract more organic traffic. This involves creating high-quality content, using relevant keywords, building backlinks, and ensuring a positive user experience. SEO is a continuous process that requires ongoing effort and adaptation to the ever-changing search engine algorithms.
Conclusion: Search Engines as Information Gateways
In conclusion, search engines play a critical role in connecting users with the vast amount of information available on the internet. What do search engines do? They crawl the web, index the content, rank the results, and answer users’ queries. By understanding these core functions, individuals and businesses can better utilize search engines to achieve their goals. As the internet continues to evolve, search engines will undoubtedly continue to adapt and improve, remaining the primary gateway to information for billions of people around the world. The complexity behind a seemingly simple search bar is a testament to the ongoing innovation in computer science and information retrieval. The future of search engines likely involves even more sophisticated AI and machine learning, enabling them to understand user intent better and provide even more personalized and relevant results. We can expect search engines to become even more integrated into our daily lives, anticipating our needs and providing information proactively. The continuous improvements in search engine technology will only enhance our ability to access and utilize the world’s knowledge.