The Ultimate Guide to Generator Auto Start Systems: Ensuring Uninterrupted Power
In today’s world, a reliable power supply is not just a convenience; it’s a necessity. From hospitals and data centers to homes and small businesses, a power outage can lead to significant disruptions, financial losses, and even life-threatening situations. This is where generator auto start systems come into play. These systems provide a seamless transition to backup power, ensuring that critical operations continue without interruption. This article provides a comprehensive overview of generator auto start systems, exploring their functionality, benefits, components, and considerations for choosing the right system.
What is a Generator Auto Start System?
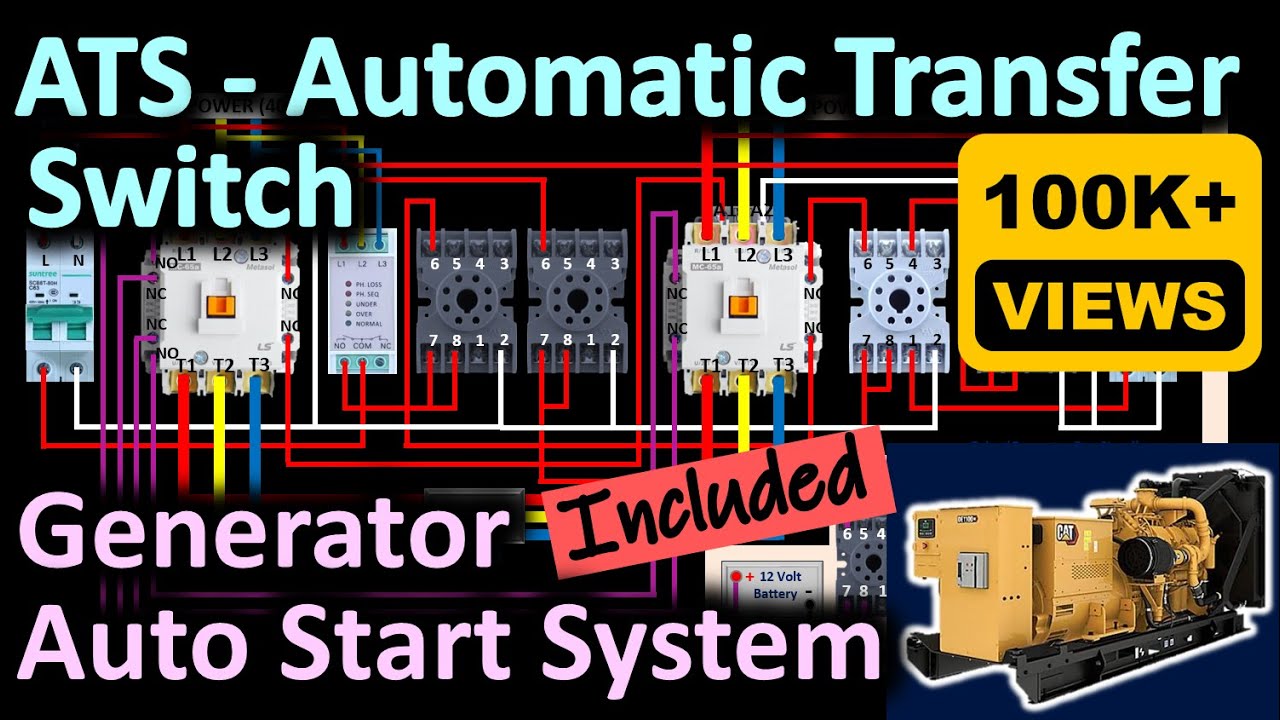
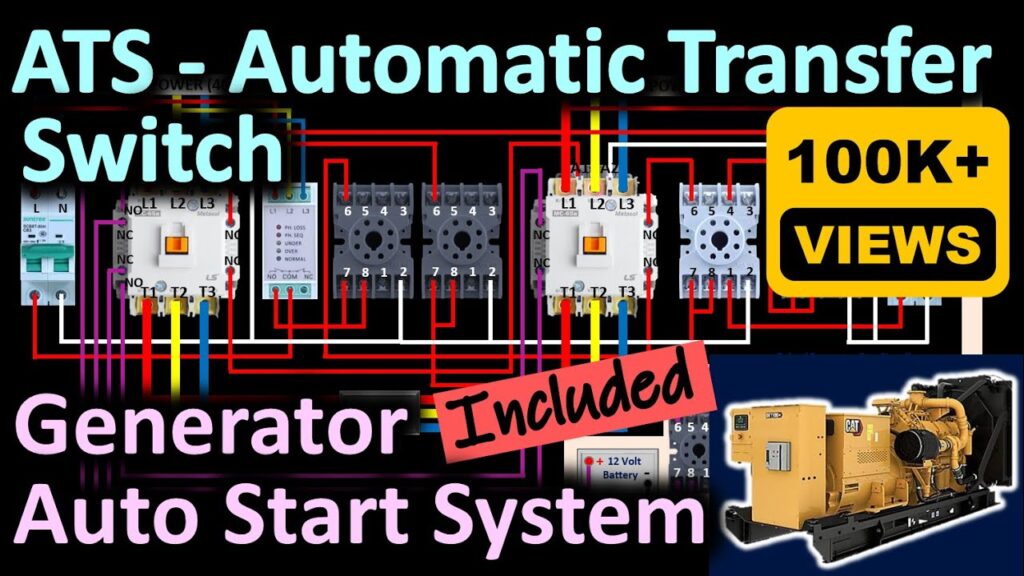
A generator auto start system, often referred to as an automatic transfer switch (ATS), is a device that automatically starts a standby generator when it detects a power outage from the main utility grid. The system monitors the incoming power and, upon detecting a loss of power, initiates the startup sequence for the generator. Once the generator is running and providing stable power, the ATS switches the load from the utility grid to the generator. When utility power is restored, the ATS automatically switches the load back to the utility grid and shuts down the generator, often after a cool-down period to prolong its lifespan.
How Does a Generator Auto Start System Work?
The functionality of a generator auto start system can be broken down into several key stages:
- Power Monitoring: The ATS continuously monitors the voltage and frequency of the incoming utility power.
- Outage Detection: If the utility power falls below a preset threshold or is completely lost, the ATS detects this condition.
- Generator Start-Up: Upon detecting a power outage, the ATS sends a signal to the generator to start. This typically involves engaging the starter motor and initiating the fuel supply.
- Power Stabilization: Once the generator is running, the ATS waits for the generator to reach a stable voltage and frequency.
- Load Transfer: After stabilization, the ATS switches the electrical load from the utility grid to the generator.
- Power Restoration Monitoring: The ATS continues to monitor the utility power.
- Return to Utility Power: When the utility power is restored and remains stable for a predetermined period, the ATS switches the load back to the utility grid.
- Generator Shut-Down: After the load is transferred back to the utility grid, the ATS shuts down the generator, often after a cool-down period.
Benefits of Using a Generator Auto Start System
The advantages of using a generator auto start system are numerous and significant:
- Seamless Power Transition: The primary benefit is the seamless transition to backup power during an outage, minimizing disruption to critical operations.
- Reduced Downtime: By automatically starting the generator, the system eliminates the need for manual intervention, significantly reducing downtime.
- Protection of Equipment: A stable and consistent power supply protects sensitive electronic equipment from damage caused by power surges or fluctuations.
- Increased Productivity: Reduced downtime translates to increased productivity for businesses and organizations.
- Enhanced Safety: In critical applications such as hospitals, a generator auto start system ensures that life-support equipment continues to function during a power outage, enhancing patient safety.
- Convenience: For residential users, an auto start system provides peace of mind, knowing that their home will be automatically powered during an outage, even when they are away.
Key Components of a Generator Auto Start System
A typical generator auto start system consists of the following key components:
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): The core component that monitors power, detects outages, and switches the load between the utility grid and the generator.
- Standby Generator: The source of backup power, typically powered by gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane.
- Control Panel: Provides monitoring and control functions for the generator and the ATS.
- Battery and Charger: Provides power for the generator’s starting system.
- Wiring and Connections: Essential for connecting the various components of the system.
Types of Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS)
There are several types of ATS available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Open Transition (Break-Before-Make): This is the most common type of ATS. It breaks the connection with the utility grid before connecting to the generator, ensuring that the two power sources are never connected simultaneously.
- Closed Transition (Make-Before-Break): This type of ATS briefly connects both the utility grid and the generator before disconnecting from the utility grid. This allows for a seamless transfer of power without any interruption, but it requires careful synchronization between the two power sources.
- Soft Loading: This type of ATS gradually transfers the load between the utility grid and the generator, minimizing stress on the generator and the connected equipment.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Generator Auto Start System
Selecting the right generator auto start system requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Power Requirements: Determine the total power requirements of the equipment and appliances that need to be powered during an outage. This will help determine the appropriate size of the generator.
- Type of Fuel: Consider the availability and cost of different fuel types, such as gasoline, diesel, natural gas, and propane.
- Load Type: Different types of loads (e.g., resistive, inductive, capacitive) may require different types of ATS.
- Transfer Time: Consider the acceptable transfer time between the utility grid and the generator. Critical applications may require a faster transfer time.
- Installation Requirements: Consider the installation requirements, including space, ventilation, and electrical connections.
- Budget: Determine your budget for the system, including the cost of the generator, ATS, installation, and maintenance.
- Maintenance Requirements: Understand the maintenance requirements of the generator and the ATS, including regular inspections, oil changes, and filter replacements.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the reliable operation of a generator auto start system. Installation should be performed by a qualified electrician, following all applicable codes and regulations. Regular maintenance should include:
- Regular Inspections: Inspect the generator and ATS for any signs of damage or wear.
- Oil Changes: Change the generator’s oil according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Filter Replacements: Replace the generator’s air, fuel, and oil filters as needed.
- Battery Maintenance: Check the battery’s voltage and condition, and replace it if necessary.
- Load Testing: Periodically test the system under load to ensure that it is functioning properly.
Generator Auto Start in Various Applications
Generator auto start systems are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Residential: Providing backup power for homes during power outages.
- Commercial: Ensuring uninterrupted power for businesses, offices, and retail stores.
- Industrial: Supporting critical operations in factories, manufacturing plants, and data centers.
- Healthcare: Maintaining power for hospitals, clinics, and nursing homes.
- Telecommunications: Keeping communication networks operational during power outages.
- Emergency Services: Powering emergency response centers and communication systems.
The Future of Generator Auto Start Technology
The technology behind generator auto start systems continues to evolve, with advancements in areas such as:
- Smart Grid Integration: Integrating with smart grids to optimize power usage and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Using remote monitoring and control systems to monitor the system’s performance and make adjustments as needed.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Implementing advanced diagnostics to detect potential problems before they cause a failure.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Developing more fuel-efficient generators to reduce operating costs and emissions.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with proper installation and maintenance, issues can sometimes arise with generator auto start systems. Some common problems and their potential solutions include:
- Generator Not Starting: Check the fuel supply, battery, and starter motor.
- Generator Shutting Down Prematurely: Check for overheating, low oil pressure, or other fault conditions.
- ATS Not Transferring Load: Check the ATS settings, wiring, and control panel.
- Warning Lights or Alarms: Consult the generator’s manual for troubleshooting information.
A generator auto start system is a critical investment for anyone who relies on a continuous and reliable power supply. By understanding the functionality, benefits, components, and considerations involved in choosing the right system, you can ensure that your power needs are met during any power outage. From homes to hospitals, the importance of these systems cannot be overstated. The ability to automatically switch to backup power provides peace of mind, knowing that essential operations will continue uninterrupted. Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are key to maximizing the lifespan and reliability of your generator auto start system. As technology continues to advance, these systems will become even more sophisticated and essential for maintaining power continuity in an increasingly interconnected world.
[See also: Standby Generator Installation Guide]
[See also: Choosing the Right Size Generator for Your Home]
[See also: Generator Maintenance Checklist]